- C-6&7, 6362, Pocket 6, Sector C, Vasant Kunj, New Delhi
- Mon - Sat: 16:00 - 20:00 PM
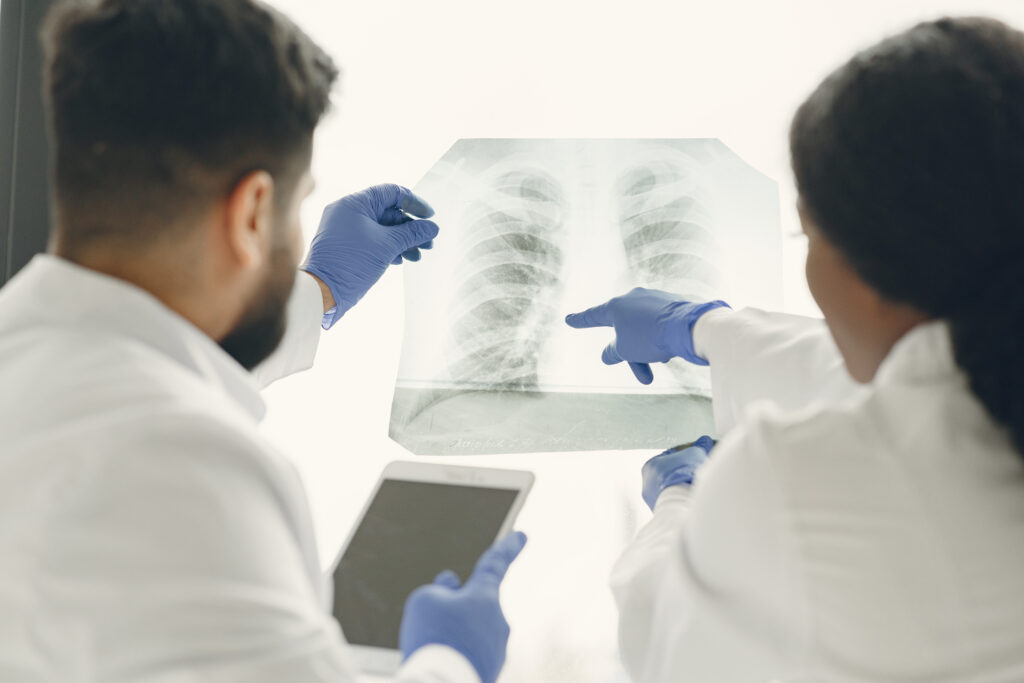
THORACOCENTESIS
Thoracocentesis is a medical procedure used to remove excess fluid or air from the pleural space, the area between the lungs and the chest wall. This intervention is often performed to alleviate symptoms associated with conditions such as pleural effusion (accumulation of fluid) or pneumothorax (presence of air). Thoracocentesis is a relatively common and minimally invasive procedure that can help relieve respiratory distress and aid in diagnostic evaluation.Thoracocentesis is a relatively common and minimally invasive procedure that can help relieve respiratory distress and aid in diagnostic evaluation.
THORACOCENTESIS PROCEDURE
Patient
Preparation:
- Explain the procedure to the patient, ensuring informed consent.
- Position the patient sitting upright or slightly reclined.
- Clean and sterilize the skin over the puncture site.
Anesthesia:
Administer local anesthesia to numb the puncture site, usually between the ribs.
Insertion of
the Needle:
- Using ultrasound guidance or anatomical landmarks, a needle is inserted through the chest wall into the pleural space.
Fluid or
Air Aspiration:
- Once the needle is in place, fluid or air is aspirated using a syringe.
- The collected fluid is sent for analysis to determine the underlying cause.
Monitoring and
Observation:
- Monitor vital signs and the patient’s respiratory status during the procedure.
- Observe for any signs of complications, such as pneumothorax or bleeding.
Completion of
Procedure:
- Remove the needle and apply a sterile dressing to the puncture site.
- Obtain post-procedure imaging to confirm resolution of any pneumothorax.
Your Lungs Deserve The best!
