- C-6&7, 6362, Pocket 6, Sector C, Vasant Kunj, New Delhi
- Mon - Sat: 16:00 - 20:00 PM
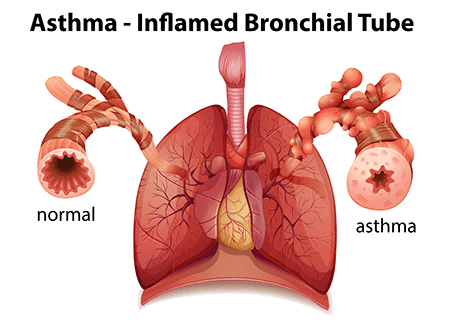
Asthma diagnosis and treatment
Bronchial asthma (or asthma) is a lung disease. Your airways get narrow and swollen and are blocked by excess mucus. Medications can treat these symptoms. Asthma diagnosis is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation of the airways, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. Asthma Diagnosis and treatment typically involves a comprehensive approach that may include medical history assessment, physical examination, lung function tests, and the development of a personalized treatment plan.
Asthma diagnosis test
Asthma diagnosis test involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and various tests. Here are the key components of asthma diagnosis test:
Medical History:
- Your doctor will ask detailed questions about your symptoms, including the nature of coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
- Information about the frequency and duration of symptoms, triggers, and any family history of asthma or other respiratory conditions will be explored.
Physical Examination:
- A thorough physical examination, especially focusing on the respiratory system, will be conducted. This may involve listening to your lungs with a stethoscope to detect any wheezing or other abnormal sounds.
Lung Function Tests:
- Spirometry: This is a common and important test for asthma diagnosis. It measures how much air you can breathe out and how fast you can do it. It helps assess the presence and severity of airflow obstruction. Spirometry is often performed before and after using a bronchodilator to see if there is a reversible component to the airflow obstruction.
- Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) Measurement: those tests involves using a peak flow meter to measure the maximum speed at which you can exhale air. Regular monitoring of peak flow at home can help track changes in lung function.
Bronchial Provocation Tests:
- These tests inhaling substances that can trigger bronchoconstriction to assess airway responsiveness. Methacholine challenge tests are an example.
Allergy Testing:
- If allergies are suspected to be a trigger for asthma, skin or blood tests may be performed to identify specific allergens.
Chest X-ray or CT Scan:
- Imaging studies like chest X-rays or CT scans may be done to rule out other respiratory conditions or complications.
Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) Test:
- test measures the level of nitric oxide in the breath, which can be elevated in people with allergic or eosinophilic asthma.
Blood Tests:
- Blood tests may be done to check for elevated levels of eosinophils, which are a type of white blood cell associated with allergic inflammation.
Exercise Challenge Test:
- This test evaluates the impact of exercise on lung function and can help diagnose exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, which is common in asthma.
asthma treatment
asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. While there’s no cure for asthma, there are effective asthma treatment that can manage symptoms and prevent attacks.
asthma Treatment options for bronchial asthma fall into two main categories:
Quick-relief medications: medications act fast to relieve symptoms during an asthma attack. They typically come in inhalers and work by relaxing the muscles around the airways, making it easier to breathe.
Short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs): the most common type of quick-relief medication. Examples include albuterol (ProAir HFA, Ventolin HFA) and levalbuterol (Xopenex, Xopenex HFA). SABAs work within minutes to open up the airways and relieve symptoms.
Long-term control medications: These are the medications are taken daily to prevent asthma attacks and control inflammation in the airways. They take longer to work than quick-relief medications, but they can significantly improve asthma control over time.
Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS): the mainstay of long-term asthma control. They reduce inflammation in the airways, making them less likely to narrow and cause symptoms. ICS come in different strengths and delivery devices, such as metered-dose inhalers (MDIs), dry powder inhalers (DPIs), and nebulizers.
Long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs): These medications work like SABAs, but they last much longer, typically for 12 hours or more. They’re often combined with ICS in a single inhaler for easier use and better asthma control.
asthma attack treatment
During an asthma attack treatment, it’s crucial to stay calm and take immediate action to relieve symptoms. Here’s a safe and effective guide:
1. Stay Calm and Slow Down: Panicking can worsen symptoms. Take deep, slow breaths to stabilize your breathing.
2. Use Your Rescue Inhaler: If prescribed, take puffs from your quick-relief inhaler (usually blue) as directed by your doctor. Repeat every few minutes if needed, but follow your doctor’s instructions or the inhaler’s label.
3. Sit Up or Stand Up: This opens your airways more effectively than lying down.
4. Loosen Restrictive Clothing: Tight clothing can worsen breathing difficulties.
5. Seek Medical Attention if Symptoms Worsen: If your symptoms don’t improve within 10-15 minutes of using your inhaler, or if they become severe (blue lips, extreme difficulty breathing, confusion), call emergency services immediately.
BOOK CONSULTATION NOW
Get in touch effortlessly. Whether you’re seeking expert advice, scheduling an appointment, or have inquiries about our services, our responsive and caring team is here to assist. Your journey to optimal health begins with a simple message.
6362, Mehrauli Mahipalpur Rd, Pocket 6, Sector C, Vasant Kunj, New Delhi,
